[ad_1]
Trojanized versions of legitimate applications are being used to deploy evasive cryptocurrency mining malware on macOS systems.
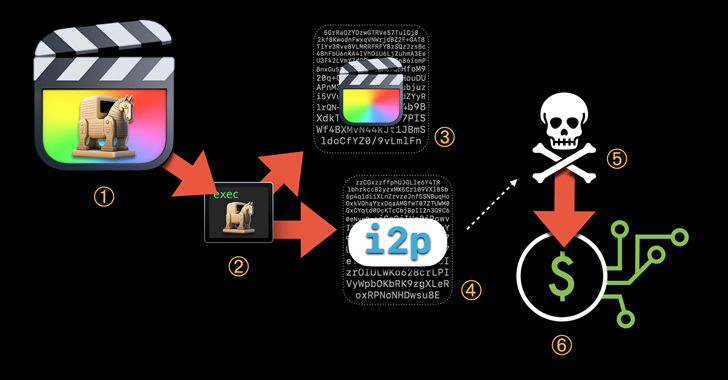
Jamf Threat Labs, which made the discovery, said the XMRig coin miner was executed as Final Cut Pro, a video editing software from Apple, which contained an unauthorized modification.
“This malware makes use of the Invisible Internet Project (i2p) […] to download malicious components and send mined currency to the attacker’s wallet,” Jamf researchers Matt Benyo, Ferdous Saljooki, and Jaron Bradley said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
An earlier iteration of the campaign was documented exactly a year ago by Trend Micro, which pointed out the malware’s use of i2p to conceal network traffic and speculated that it may have been delivered as a DMG file for Adobe Photoshop CC 2019.
The Apple device management company said the source of the cryptojacking apps can be traced to Pirate Bay, with the earliest uploads dating all the way back to 2019.
The result is the discovery of three generations of the malware, observed first in August 2019, April 2021, and October 2021, that charts the evolution of the campaign’s sophistication and stealth.
One example of the evasion technique is a shell script that monitors the list of running processes to check for the presence of Activity Monitor, and if so, terminate the mining processes.
The malicious mining process banks on the user launching the pirated application, upon which the code embedded in the executable connects to an actor-controlled server over i2p to download the XMRig component.
The malware’s ability to fly under the radar, coupled with the fact that users running cracked software are willingly doing something illegal, has made the distribution vector a highly effective one for many years.
Apple, however, has taken steps to combat such abuse by subjecting notarized apps to more stringent Gatekeeper checks in macOS Ventura, thereby preventing tampered apps from being launched.
“On the other hand, macOS Ventura did not prevent the miner from executing,” Jamf researchers noted. “By the time the user receives the error message, that malware has already been installed.”
“It did prevent the modified version of Final Cut Pro from launching, which could raise suspicion for the user as well as greatly reduce the probability of subsequent launches by the user.”
[ad_2]
Source link